Be yourself; Everyone else is already taken.
— Oscar Wilde.
This is the first post on my new blog. I’m just getting this new blog going, so stay tuned for more. Subscribe below to get notified when I post new updates.
Be yourself; Everyone else is already taken.
— Oscar Wilde.
This is the first post on my new blog. I’m just getting this new blog going, so stay tuned for more. Subscribe below to get notified when I post new updates.
In Java we can use a Comparable or Comparator interface to sort a collection. Both interfaces have some differences you should know in order for you to make the right decision.
Comparable Interface
Comparator Interface
Map Interface
What is a map in java? In java map is an interface that extends the collection interface. A map structures its elements in a unique key value pair by using a hash table data structure. A map is unordered by default. Map can be implemented by TreeMap, HashMap, and LinkedHashMap classes.
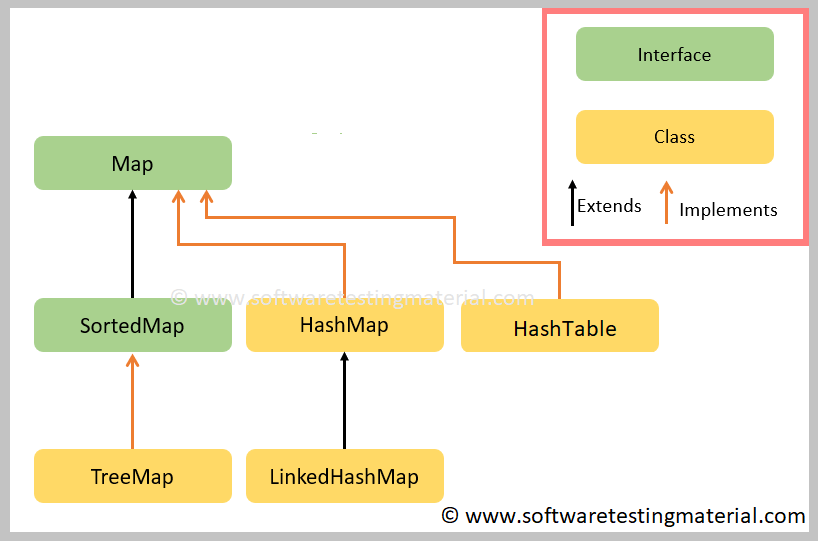
HashTable
A HashTable implements the map interface. HashTable allows doesn’t allow null key or values. HashTable is synchronized, which can be useful for threaded applications.
HashMap
A HashMap implements the map interface. HashMap is an implementation of a hash table data structure. It allows one null key in an element. HashMap is non-synchronized, because of this it’s faster than a HashTable.
LinkedHashMap
The LinkedHashMap class extends HashMap. A LinkedHashMap maintains insertion order unlike a HashMap.
TreeMap
TreeMap implements SortedMap interface which extends the map interface. SortedMap maintains the key value pairs in a sorted ascending order by default. The TreeMap uses a tree data structure, because of tree structure its access and retrieval time are fast O(log n) logarithmic time complexity. Also, TreeMap doesn’t take null keys
Set Interface
What is a set in java? Well a set is an interface that extends the collection interface. A set structure, represents an unordered set of elements that only allows unique elements, no duplicates and at most one null element. In ordered to create a set collection we have to implement the set interface. There are 3 classes that implement set, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet.
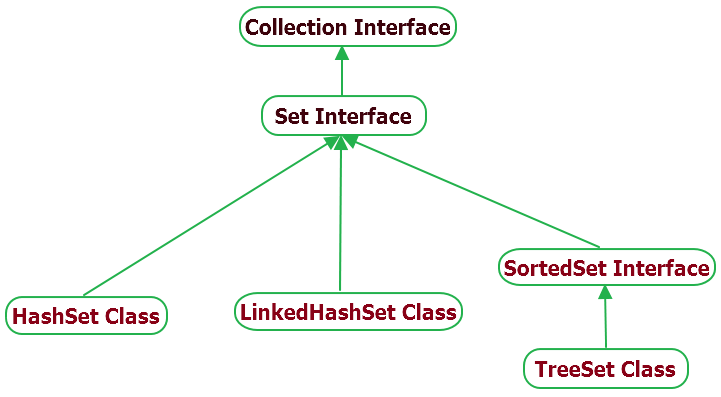
HashSet
HashSet class implements the set interface. It uses a hash table data structure to store elements. A HashSet uses a hash function to store the elements. This allows for fast access operation O(1) constant time complexity.
LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet extends the hashSet. The only difference is that it maintains the insertion ordered unlike a HashSet which is unordered.
TreeSet
TreeSet implements the SortedSet interface which extends from the Set interface. The SortedSet elements are sorted by ascending order by default. The TreeSet uses a tree data structure, because of tree structure its access and retrieval time are fast O(log n) logarithmic time complexity. Also, TreeSet doesn’t take null values
What is a list in java? Well, a list is an interface that extends the collection interface. A list structure’s our elements in insertion. A list alone is not enough to create a collection. We have to implement this collection interface, there are 3 different classes the implement list, ArrayList, LinkedList, and Vector.
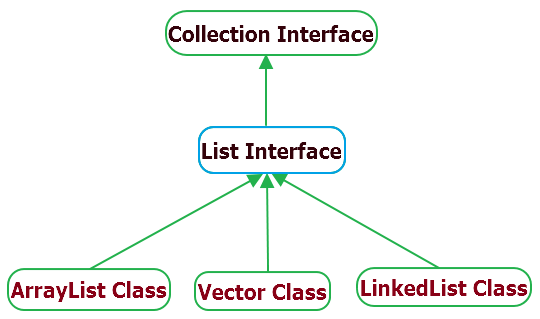
ArrayList
The arraylist class uses a dynamic array structure allowing it to grow by 50% its size when full, does not contain a fixed size. Elements from an array list can be randomly accessed. It is also non-synchronize.
Vector
The vector is very similar to the array list and the only differences are:

LinkedList
A linkedlist implements a doubly linked list which, structures each element as a node with a pair of reference pointers to the next node and previous node. Data manipulation operations like insertion and deletion is very fast because we only need to change the pointers only taking O(1) constant time complexity.

Q1: What is a collection?
A java collection is a container that holds objects in a certain structure, is an implementation of a data structure. Many operations can be perform on the data such.
Q: What operations can be perform on a collection?
All operations, sorting, insertion, manipulation and deletion.
Q: What are the benefits of a using a collection?
Q: What is the main difference between list and Arraylist collection?
List is an interface which extends the collection interface, its data structure stores the collection of objects in insertion order, allowing duplicates.
Arraylist is a class that implements list and it uses a dynamic array meaning its size is not fixed. Elements in an Arraylist can be randomly accessed.
Yes, JavaScript is case sensitive.
//incorrect syntax
Var num=4;
//correct syntax
var num=4;
Q1: What is CSS?
Cascading Style Sheets is a web defining language for html elements and is also known as XHTML. It is used to style html pages and allows to have all styling separate from html file.
Q2: What are the 3 ways CSS can be integrated in HTML?
Q1: What is HTML?
Hyper Text Markup Language is the language of the web. It is the standard formatting text and is used to create organize webpages, by allowing text to turn into images, tables and links.
Q2: What are tags?
Tags are used in html to format content, and it is wrapped in angle brackets and can have closing tag. ex: <p> hey</p>
Q3: Do all tags have a closing tag?
In html not all tags have a closing tag, for example <img> tag doesn’t have a closing tag.
Q4: How many different types of heading does HTML have?
HTML contains 6 different heading tags from <h1> through <h6>. The heading sizes get smaller as you go higher.
The Adapter pattern is a structural pattern that allows two objects with incompatible interfaces to interact. Adapter pattern is also known as a wrapper.
UML Diagram Example

RoundHole that has a function called fits() that takes in a RoundPeg object and returns if it fits. We also have a SquarePeg class that creates incompatible objects, lucky we have our SquarePegAdapter class that implements the roundPeg and that takes in a a SquarePeg object and making it compatible with RoundHole class
The singleton design pattern is one of a kind, The singleton is a creational pattern that makes sure you only have one instance of a class, while providing global access to this object.
Requirements:
UML Diagram example
