Set Interface
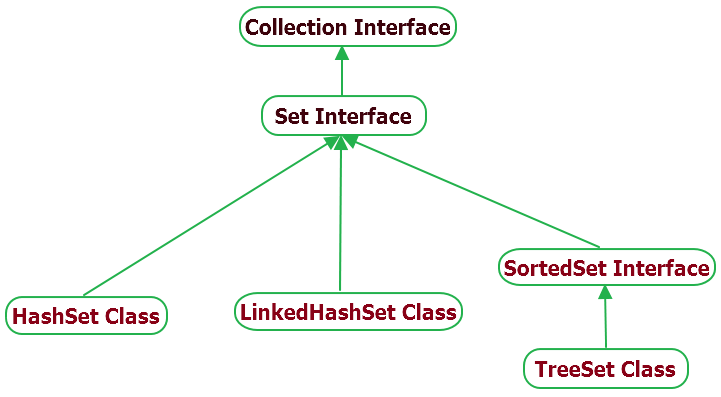
What is a set in java? Well a set is an interface that extends the collection interface. A set structure, represents an unordered set of elements that only allows unique elements, no duplicates and at most one null element. In ordered to create a set collection we have to implement the set interface. There are 3 classes that implement set, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet.
HashSet
HashSet class implements the set interface. It uses a hash table data structure to store elements. A HashSet uses a hash function to store the elements. This allows for fast access operation O(1) constant time complexity.
LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet extends the hashSet. The only difference is that it maintains the insertion ordered unlike a HashSet which is unordered.
TreeSet
TreeSet implements the SortedSet interface which extends from the Set interface. The SortedSet elements are sorted by ascending order by default. The TreeSet uses a tree data structure, because of tree structure its access and retrieval time are fast O(log n) logarithmic time complexity. Also, TreeSet doesn’t take null values