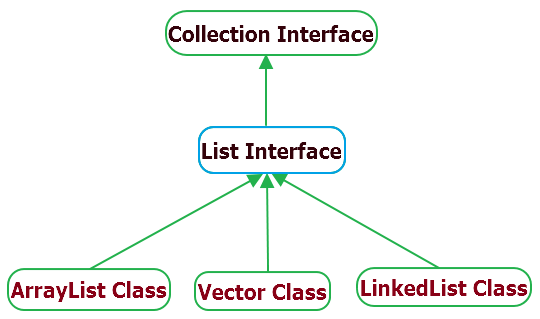
What is a list in java? Well, a list is an interface that extends the collection interface. A list structure’s our elements in insertion. A list alone is not enough to create a collection. We have to implement this collection interface, there are 3 different classes the implement list, ArrayList, LinkedList, and Vector.
ArrayList
The arraylist class uses a dynamic array structure allowing it to grow by 50% its size when full, does not contain a fixed size. Elements from an array list can be randomly accessed. It is also non-synchronize.
Vector
The vector is very similar to the array list and the only differences are:
- Vector is synchronized
- legacy class
- Contains more methods that are not apart from the collections framework
- Increases its size by doubling its size

LinkedList
A linkedlist implements a doubly linked list which, structures each element as a node with a pair of reference pointers to the next node and previous node. Data manipulation operations like insertion and deletion is very fast because we only need to change the pointers only taking O(1) constant time complexity.
