Q1: What is SQL?
The Structure Query Language is the standard language for relational data bases. SQL uses tables to allow for setting or retrieving data from a database.
Q2: Define DDL, DML and DCL
- DDL (Data Definition Language) – It allows you to perform sql commands that define the database scheme. Some of these commands are create, alter, drop.
- DML ( Data Manipulation Language) – The DML consist of commands that manipulate data in the database. It helps you to insert, update, delete and retrieve data from the database.
- DCL ( Data Control Language) – It allows you to control access to the database. Example – Grant, Revoke access permissions.
Q3: What is a DBMS?
A Data Base Management System is a software that sits in between the user and database, allowing the user to interact with the database for manipulating and retrieving data. It ensures that our data is consistent, organized and is easily accessible.
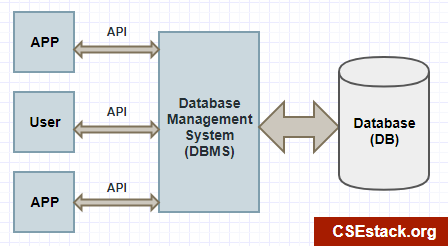
Q4: What are the 2 types of DBMS?
- Relational Database Management System: The data is stored in relations, which are tables. MySQL
- Non-Relational Database Management System: The data is not stored in relations/ tables. MongoDB

Q5: What are tables, fields and records?
Tables are a collection of data in the form of rows and columns. You first need to create the schema of the table before you can insert entries. Schema of the table is the skeleton of the table. Fields are the columns of the tables and records/ entries are the rows of the tables.
Q6: What are Constraints in SQL?
Constraints are rules given to fields when creating or altering a table.
- NOT NULL – Restricts NULL value from being inserted into a column.
- CHECK – Verifies that all values in a field satisfy a condition.
- DEFAULT – Automatically assigns a default value if no value has been specified for the field.
- UNIQUE – Ensures unique values to be inserted into the field.
- INDEX – Indexes a field providing faster retrieval of records.
- PRIMARY KEY – Uniquely identifies each record in a table.
- FOREIGN KEY – Ensures referential integrity for a record in another table.
Q7: What is a Primary Key?
Primary Key is a field or a set of fields that uniquely represents a record in a table. It must contain unique values and has an implicit NOT NULL constraint. A table can only have one primary key, comprised of a single field or multiple fields.
id int primary key
#multiple fields as a primary key
id int,
name varchar(50) not null,
constraint pk
primary key(id, name)
Q8: What is a Foreign Key?
A foreign key is a constraint on a field that refers to another primary key of another table.
film_id int foreign key (film_id)
references film(film_id)
Q9: What is the keyword for finding common records from two table?
We can use the INTERSECT command to find common records between two tables. MySQL doesn’t support this command use inner join instead.
select first_name from actor
INTERSECT
select first_name from customer;
Sources
https://www.javatpoint.com/sql-interview-questions
https://www.interviewbit.com/sql-interview-questions/